 What
Is the Atmosphere?
What
Is the Atmosphere?
The atmosphere is air that is organized into thin layers, which form a protective blanket between the Earth and the vacuum of space. These layers are distinguished mainly by density, temperature, and slight changes in the mixture of gases, the composition of the air.
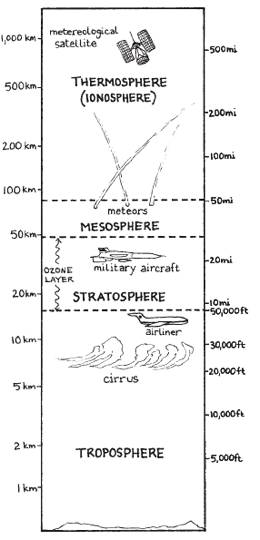
The air we breathe is the part of the atmosphere known as the troposphere - a layer that rises 10–18 km above the Earth's surface.
The atmosphere is most dense closest to the Earth's surface. This is because air is affected by gravity, which pulls it toward the Earth. About 80% of all the air molecules is found in the troposphere. This region supports life and contains most of the weather activity influencing Earth. The density of gases decreases as the distance from the Earth's surface increases.
Above the troposphere, up to about 50 km, is the stratosphere that contains much of the ozone found in the atmosphere. Although this "ozone layer" contains only very small concentrations of ozone molecules (O3) - about 10 ppm (parts per million) - it performs the important function of protecting Earth from dangerous high-energy ultraviolet radiation coming from the Sun. These few ozone molecules absorb UV radiation and then re-emit the energy in all directions as lower-energy infrared radiation. In this way the ozone layer protects us from sunburn, skin cancer, and many eye diseases, and it enables vegetation and all other life to survive.
Above the stratosphere are the mesosphere and the thermosphere. The mesosphere extends from approximately 50 km to approximately 80 km above the Earth's surface. The mesosphere contains the coldest portion of the atmosphere with an average of -90¼C. The thermosphere, or "heat sphere," extends above the mesosphere to approximately 480 km above the Earth's surface. Intense electromagnetic radiation from the Sun reaches this "sphere" and causes the molecules and atoms (mainly nitrogen, oxygen, and O2) to vibrate. This vibration results in individual molecules and atoms of high energy, but because the density of the atoms and molecules is so low, the amount of heat is actually relatively low.