- Add or remove heat: If a reaction is endothermic then adding heat will increase it's rate, if exothermic the reverse reaction will be favored.
- Add or remove various reactants or products: because reactions occur when molecules collide, adding more of one type of molecule will favor its collision with other molecule, thus increasing the probability that it will react.
- Raise or lower the pressure for reactions which involve gasses: Assuming the reaction vessel remains at a constant volume the only way to respond to increased pressure would be to form fewer moles of gas. Reactions which reduce the number of gaseous molecules would be favored under increased pressure. The opposite is true for reduced pressure.
- Add a catalyst which increases the rate of one reaction over the other: if a catalyst only accelerates a reaction in one particular direction, then a new equilibrium will be reached under these new conditions.
| 2 NO2
|
|
| brown | colorless |
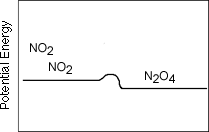
As written this reaction is exothermic from left to right
and endothermic from right to left.
| |
-
What would happen if you heated this system?
-
What would happen if you increased the pressure on this system?
-
What would happen if you added more N2O4?
-
What would happen if you removed N2O4?
-
What would happen if you added a catalyst?