Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR)
- Electromagnetic Radiation is a type of energy that travels in waves.
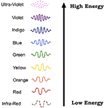
- Types of EMR

- Radio waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared
- Visible light
- Ultra Violet
- X-Rays
- Gamma Rays
- Handout: Electromagnetic
Waves
- To talk of a particular kind of energy we can discuss the energy, wavelength,
or frequency of the wave
 .
.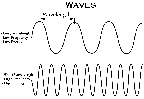
- Wavelength is the distance from the peak of one wave to the
peak of another.
- Frequency is the the number of waves per second that a stationary observer
would count while the wave is passing by.
- Energy, frequency, and wavelength are all interrelated due to the fact
that all EMR travels at the same speed. As wavelength decreases, frequency
increases, and energy increases.
- Nature of Light
- Light is just the range of electromagnetic radiation that had
the correct wavelengths (or frequency or energy) to excite the molecules
in cells at the back of our eyes. When these cells get excited they send
electrical nerve impulses to our brain and we "see".
- Our eyes can combine multiple colors (wavelengths) of light to see one
color. White light is the combination of all colors.
- Prisms and diffraction gratings can separate light which is a mixture
into its component parts.

 .
.