In chemical notation the reaction is written: 2 H2 + O2 --------------------------------> 2 H2O
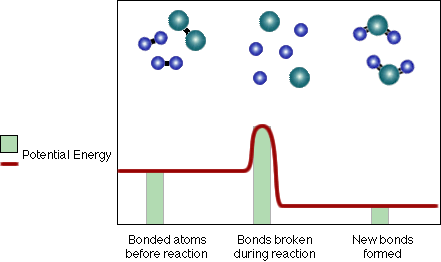
Notice that the proportion of heat and light energy after the new bonds form is greater than it was before. In other words, heat and light energy are released as the reaction is completed. On average the bonds in the Water (H-O-H) molecules are stronger than those of the Hydrogen (H-H) and Oxygen (O-O) molecules. Because the (H-O) bonds in water are stronger, they have less potential energy, therefore some of that chemical potential energy must be converted to heat and light.
Also, note that the reaction could be run in reverse, but heat and light energy must be absorbed and converted to chemical potential energy in order to break up water to form Hydrogen and Oxygen.
If we just graph the potential energy you will see a graph that looks like this:
- Film: Releasing energy in ionic bond formation.
- Film: Releasing energy in molecular bond formation.
- In summary, during a reaction some chemical bonds are broken and new
ones are formed. In order for a chemical reaction to produce heat energy,
the new bonds must be stronger or more stable than the old bonds. If this
is true, some of the potential energy that was present when atoms were
more weakly bonded together must be released as heat and/or light to form
the new more stable bonds. A chemical reaction happens in several steps:
- First, energy of some form, usually heat or light, is absorbed by two bonded atoms. This causes them to separate, breaking their chemical bond and increasing their chemical potential energy. (Some of the heat or light energy was converted to chemical potential energy.)
- Then, two different atoms collide with each other. As these two atoms get closer together, they begin to form a chemical bond, decreasing the chemical potential energy and releasing heat and/or light energy.