- He was a professor of Chemistry. at the University of St. Petersburg in Russia and was confronted with the problem of how to teach about the various elements known at that time. He decided to organized the elements by arranging them into groups that reacted similarly.
- He also noticed that various properties would repeat "periodically" so he arranged a table of elements order of atomic mass such that properties would change regularly if you moved across a row while maintaining groups with similar chemical properties in a column.
- Go to: http://www.periodic.lanl.gov/mendeleev.htm to see a version of Mendeleev's first table.
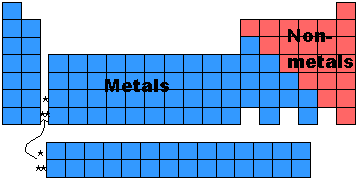
- All the elements in a group (or column) are called families.
- Group 8: The Noble Gases, don't react with other elements.
- Group 1: The Alkali Earth Metals, all react with water in the following
manner
2 Li + H2O ---> H2 + 2 LiOH
2 Na + H2O ---> H2 + 2 NaOH
...
2 Fr + H2O ---> H2 + 2 FrOH
- These are just a few examples of how Mendeleev organized the columns or families.
- As you move across a row various properties change regularly
click on the images below to see a visualization of the various properties.
All of these images are from www.webelements.com,
one of the best periodic table sites on the web.
Periodic Trends 



Summary of Trends